10th Class SA1 Question Paper 2017: We provide you with all the required PDFs for Class 10 SA1 Question Papers 2017, available for Telugu English Medium. All textbooks, materials, and notes required for class 10 will be provided to you for free. If you find the PDFs here useful, share them with your friends.
10th Class SA1 Question Paper 2017
You can find all the 10th Class SA1 Question Paper 2017 in the table below. Also, if you need PDFs, then let us know in the comment box given below.
AP 10th Class Maths Notes Real Numbers
AP Board Solutions Class 10 Maths and All Textbooks
Question 1:
What is humidity? (AP March 2015)
Answer:
Humidity:
The amount of water vapor present in the air is called humidity.
Question 2:
Define latent heat of Fusion. (AP March 2016)
Answer:
Latent heat of Fusion:
At constant temperature, the heat energy required to convert one gram of solid completely into liquid is called latent heat of Fusion.
Question 3:
While drinking water, Rama spilled some water on the floor. After some time, the water disappeared from the floor. What happened to the water? (TS June 2015)
Answer:
The water disappeared due to evaporation because we know that as the surface area increases rate of evaporation also increases. So water molecules escape from the floor to air.
Question 4:
Give an example to explain that evaporation is a cooling process. (TS March 2016)
Answer:
The examples to explain that evaporation is a cooling process are:
- Drying of wet clothes
- When the floor is washed with water, the water on the floor disappears.
- Sweating, etc.
Question 5:
Let heat is not lost by any other process between two objects in thermal contact, “Net heat lost (by hot body) = Net heat gain (by cold body).” above statement indicates a principle. Write the name of that principle. (AP March 2019)
Answer:
Principle of method of mixtures.
Question 6:
Convert 25°C into Kelvin scale. (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Answer:
25°C = (273 + 25) K = 298 K
Question 7:
Given a beaker with water, a thermometer and a stand, draw the arrangement of an experiment to measure boiling point of water. (AP SA-1:2019-20)
Answer:
[Drawing arrangement]
Question 8:
Define heat.
Answer:
Heat: Heat is a form of energy which is transferred from one body to the other body due to the difference in their temperature.
Question 9:
What is meant by thermal equilibrium?
Answer:
Thermal Equilibrium:
Two bodies are at the same temperature then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Question 10:
Define dew.
Answer:
Dew:
The water droplets condensed on surface are known as dew.
Question 11:
What is boiling?
Answer:
Boiling is a process in which the substance changes from liquid to gas.
Question 12:
What is melting?
Answer:
Melting:
The process in which the substance changes from solid to liquid state is called melting.
Question 13:
What are the different energies possessed by the system (body or material)?
Answer:
- Linear kinetic energy
- Rotational kinetic energy
- Vibrational energy
- Potential energy and Internal energy (I.E).
Question 14:
Why does samosa seem to be cool but hot when we eat?
Answer:
Because the curry inside samosa contains ingredients with higher specific heats.
Question 15:
On which factors does the rate of evaporation depend?
Answer:
- Surface area
- Temperature
- The amount of vapor already present in the surrounding air.
Question 16:
What is the value of latent heat of vaporization of water?
Answer:
Latent heat of vaporization of water = 540 cal/gm. (or) 2.26 × 10^6 J/kg
Question 17:
What is the value of latent heat of fusion of ice?
Answer:
Latent heat of fusion of ice is 80 cal/gm. (or) 3.26 × 10^5 J/kg
Question 18:
Give some liquids which solidify (convert into solid) in the winter season.
Answer:
Coconut oil, ghee are some liquids which solidify in the winter season.
Question 19:
What is freezing?
Answer:
Freezing:
The process in which the substance changes from liquid to solid state by losing some energy from it is called freezing.
Question 20:
Which will have a lower temperature when we take out a wooden piece and a metal piece from a fridge?
Answer:
The metal piece will have a lower temperature as compared to the wooden piece when they are taken out of the fridge.
Question 21:
When do you say there is thermal equilibrium between two bodies?
Answer:
It is said that there is thermal equilibrium between two bodies when there is no transfer of heat energy between them. (OR) When the temperature between two bodies is the same, it is said that there is thermal equilibrium between them.
Question 22:
What is absolute temperature?
Answer:
Temperature measured in the Kelvin scale is called absolute temperature.
Question 23:
What is latent heat of vaporization?
Answer:
At constant temperature, the heat energy required to change one gram of liquid into the gaseous state.
Question 24:
What is the boiling point?
Answer:
The temperature at which the substance changes from liquid to gaseous state at the fixed temperature is called boiling point.
Question 25:
What is the melting point?
Answer:
Melting point: The temperature at which the substance changes from solid to liquid state at constant temperature is called the melting point.
Question 26:
How is an aquatic animal able to live at poles?
Answer:
The ice has less density compared to water. So it forms a layer on the top of the water which prevents the solidification of water.
Question 27:
What are the phases of water present at 0°C?
Answer:
Two phases namely, ice and water.
Question 28:
What happens if the external pressure of the liquid increases?
Answer:
The boiling point of the liquid will increase.
Question 29:
Does ice melt below 0°C?
Answer:
Yes, if the external pressure increases it melts at low temperature.
Question 30:
What happens when two objects of the same temperature are in contact with each other?
Answer:
Heat does not flow between two objects.
Question 31:
What is the principle involved in a pressure cooker?
Answer:
The boiling point of the liquid increases with external pressure.
Question 32:
What happens to the kinetic energy of particles if we increase the temperature?
Answer:
The kinetic energy of particles increases with an increase in temperature.
Question 33:
Why does transfer of heat energy take place between systems?
Answer:
When heat energy is given to the system, internal energy increases. Similarly, internal energy decreases when heat energy flows out of the system.
Question 34:
What is internal energy?
Answer:
Internal energy: It is the energy possessed by the system by virtue of its molecular motion and molecular configuration. It is a stored energy. It depends on the temperature of the system.
Question 35:
What is transit energy?
Answer:
Transit energy: Energy possessed by a system which can cross its boundary is called transit energy. Heat and work are transit energies.
Question 36:
Where does air get vapor from?
Answer:
The vapor may come from the evaporation of water from the surfaces of rivers, lakes, ponds, and from the drying of wet clothes, sweat, and so on.
Question 37:
Why do pigs toil in the mud during hot summer days?
Answer:
They do not have sweat glands for the evaporation process. So pigs toil in the mud.
Question 38:
Why is it easy to cook food in a pressure cooker?
Answer:
As the atmospheric pressure increases, the boiling point of water increases. So we can increase the boiling point of water to 120°C in a pressure cooker. So it is easy to cook in a pressure cooker.
Question 39:
Why is water used as a coolant?
Answer:
Water has the highest specific heat. So it takes a lot of time to become hot. So it is used as a coolant.
Question 40:
How is fog formed?
Answer:
The water molecules present in vapor condense on the dust particles in the air and form small droplets of water which form a thick mist called fog.
Question 41:
Equal amounts of water are kept in a cup and in a dish. Which will evaporate faster? Why?
Answer:
The water present in the dish evaporates faster because the dish has a larger surface area. Evaporation of liquids depends on surface area.
Question 42:
Explain why dogs pant during hot summer days using the concept of evaporation.
Answer:
Dogs do not have pores on their bodies. The only place where a dog can sweat is on its foot pads and the rest of the body is covered in a fur coat. So it cannot sweat; that’s why dogs pant to keep themselves cool.
Question 43:
Same amount of heat is supplied to two liquids A and B. The liquid A shows a greater rise in temperature. What can you say about the specific heat of A?
Answer:
The specific heat of A is less than that of B because the rise in temperature is inversely proportional to the specific heat.
Question 44:
What is the specific heat of water at boiling point?
Answer:
Generally, the specific heat of water is 1. Specific heat of water at 100°C = 4.219 KJ / KgK
Question 45:
What is the equation of heat energy when changing the state?
Answer:
Q = mL
Where m = mass of the body, L = latent heat.
Question 46:
Convert 212°F into Kelvin scale.
Answer:
212°F = 100°C. So 100 + 273 = 373 K.
Question 47:
Convert 310 K into the centigrade system.
Answer:
310 – 273 = 37°C.
Question 48:
Are the processes of evaporation and boiling the same?
Answer:
No. Evaporation takes place at any temperature, while boiling occurs at a definite temperature called the boiling point.
Question 49:
Define latent heat of vaporization?
Answer:
The heat energy required to change one unit mass of liquid to gas at constant temperature is called latent heat of vaporization. L = Q/m. The value of latent heat of vaporization of water is 540 cal/gm.
Question 50:
What is meant by internal energy?
Answer:
The combination of linear kinetic energy, rotational kinetic energy, vibrational energy, and potential energy of molecules is known as the internal energy of the system.
Question 51:
Write the formula for resultant temperatures of a mixture, when V1 ml of water at T1°C is mixed with V2 ml of water at T2°C.
Answer:
Resultant temperature T = (V1T1 + V2T2) / (V1 + V2)
Question 52:
Write the equation of heat energy when changing the temperature.
Answer:
Q = m * S * ΔT
Where m = mass, S = specific heat, ΔT = change in temperature.
Question 53:
The figure shows change in state of ice from – 5°C to 110°C with temperature. What are the melting and vaporization curves?
Answer:
BC = melting
DE = vaporization curve
Question 54:
Write the principle of the method of mixtures.
Answer:
When two or more bodies are brought into thermal contact, then the heat lost by the hot body is equal to the heat gained by the cold body until they attain thermal equilibrium.
Question 55:
Evaporation is a cooling process. Why?
Answer:
During the evaporation process, the energy of the molecules inside the liquid decreases and they slow down.
Question 56:
Which factors influence the rate of evaporation of a liquid?
Answer:
The rate of evaporation of a liquid depends on surface area, temperature, pressure, and the amount of vapor present in the surrounding air.
Question 57:
What is meant by fog?
Answer:
The droplets keep floating in the air and form a thick mist which restricts visibility. This thick mist is called fog.
Question 58:
Why do we sweat while doing work?
Answer:
When we work, our body produces heat. As a result, the temperature of the skin becomes higher and the water in the sweat glands starts evaporating. This evaporation cools the body.
Question 59:
A samosa appears to be cool when touched outside but it is hot when we eat it. Why?
Answer:
A samosa appears to be cool outside but it is hot when we eat it because the curry inside the samosa contains ingredients with higher specific heats. Hence they remain hot for a long time.
Question 60:
Equal amounts of water are kept in a cup and in a dish. Which will evaporate faster? Why?
Answer:
The water present in the dish evaporates faster because the dish has a larger surface area. Evaporation of liquids depends on surface area.
Question 61:
Why is water used as a coolant in the cooling system of automobile engines?
Answer:
Due to its high specific heat, water absorbs a large amount of heat and its temperature does not rise quickly. Therefore, water is used as a coolant in the cooling system of automobile engines.
Question 62:
Why do pigs toil around in the mud?
Answer:
Pigs do not have sweat glands. Water in the mud evaporates and helps the pig to cool down from the heat. So, pigs toil in the mud during the summer.
Question 63:
Take a small glass bottle with a tight lid. Fill it with water completely without any gaps and fix the lid tightly in such a way that water should not come out of it. Put the bottle into the deep freezer for a few hours. Take it out from the fridge. You observe the glass bottle is broken. Why?
Answer:
When water freezes into ice, it expands in volume. Since the volume of ice is greater than the volume of water, the glass bottle cannot withstand the expansion force, causing it to break.
Question 64:
From the given figure, in which the thermometer mercury level increases and decreases?
Answer:
Thermometer A (in oil) increases. Thermometer B (in water) decreases.
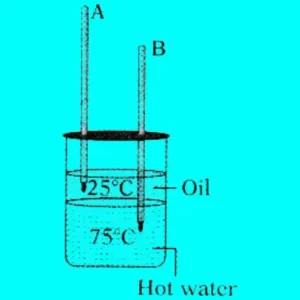
Question 65:
What materials are used to find the specific heat of a solid?
Answer:
Calorimeter, thermometer, stirrer, water steam heater, wooden box, and lead shots.
Question 66:
What is the value of the following temperatures in the Kelvin scale?
(a) 30°C (b) 70°C
Answer:
a) 30°C = 30 + 273 = 303 K
b) 70°C = 70 + 273 = 343 K
Question 67:
How much heat energy is required to raise the temperature of unit mass of material by 1°C?
Answer:
1 cal/g – °C = 1 kcal/kg – °C = 4.187 kJ/kg – °C
Question 68:
How much energy is required to turn 1 g of ice at 0°C into 1 g of water at 0°C?
Answer:
The energy required to convert 1 g of ice at 0°C into 1 g of water at 0°C is the latent heat of fusion, which is 80 cal/g.
Question 69:
What is the temperature of the mixture if 10 g of steam at 100°C is mixed with 50 g of ice at 0°C?
Answer:
To determine the final temperature, we can use the principle of conservation of energy.
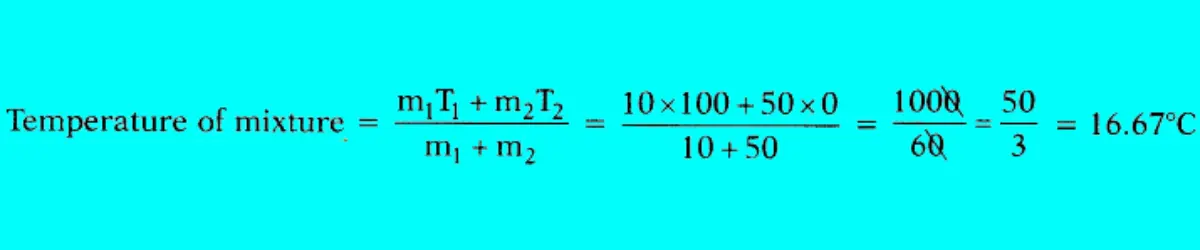
Question 70:
Boiling water at 100°C and cold water at t°C are mixed in the ratio of 3:5, and the resultant temperature is 40°C. Find the value of t.
Answer:
To find the value of �, we can use the principle of conservation of energy and the formula for the resultant temperature of a mixture.
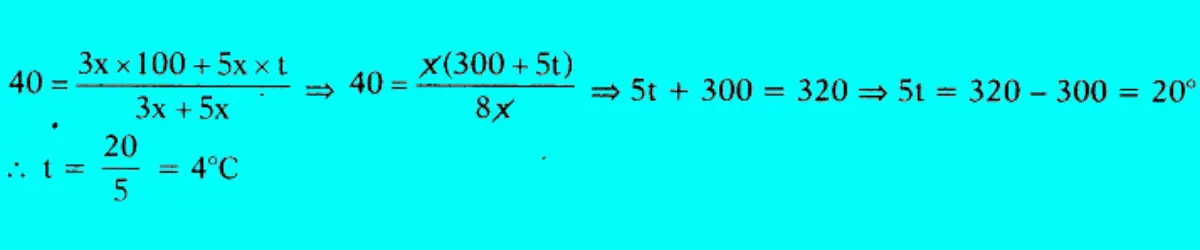
Question 71:
What amount of ice can be melted by 4000 cal of heat?
Answer:
Latent heat of fusion of ice Lf = 80 cal/g
Given that Q = 4000 cal
Q = mLf ⇒ 4000 = m × 80
∴ m = 400080 = 50 g
Question 72:
5 g of ice is at 0°C. It is converted into water at the same temperature. How much heat energy is required?
Answer:
To find the heat energy required, we can use the formula �=��, where � is the mass of ice and � is the latent heat of fusion.
Question 73:
What would be the final temperature of a mixture of 50 g of water at 20°C and 50 g of water at 40°C?
Answer:
To find the final temperature of the mixture, we can use the principle of conservation of energy and the formula for the resultant temperature of a mixture.
Question 74:
Why does the temperature of water remain constant during the change of state?
Answer:
The temperature of water remains constant during a change of state because the heat energy supplied or released during the change of state is used to overcome the intermolecular forces between the molecules, rather than increasing or decreasing the kinetic energy (temperature) of the molecules.
Question 75:
Explain why the water droplets form on the outside of a cold glass of water on a hot day.
Answer:
The water droplets form on the outside of a cold glass of water on a hot day due to condensation. When warm, moist air comes into contact with the cold surface of the glass, it cools down. As the air cools, its ability to hold moisture decreases, causing the excess moisture to condense on the surface of the glass, forming water droplets.
Question 76:
What happens to the volume of a gas when it is heated at constant pressure?
Answer:
When a gas is heated at constant pressure, its volume increases. This is because heating the gas increases the average kinetic energy of its molecules, causing them to move faster and collide more frequently with the walls of the container, thereby exerting more pressure and expanding the volume.
Question 77:
Explain why a gas cools down when it expands without doing any work.
Answer:
When a gas expands without doing any work, it performs adiabatic expansion, meaning it expands without exchanging heat with its surroundings. During adiabatic expansion, the gas molecules do work on the surrounding environment, causing them to lose kinetic energy and thus cool down.
Question 78:
Define the term “specific heat” of a substance.
Answer:
The specific heat of a substance is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of the substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin).
Question 79:
Explain why land heats up and cools down more quickly than water.
Answer:
Land heats up and cools down more quickly than water because land has a lower specific heat compared to water. This means it takes less heat energy to raise the temperature of land compared to water, but it also means land loses heat more quickly when the heat source is removed.
Question 80:
What is the significance of the triple point of water?
Answer:
The triple point of water is the unique temperature and pressure at which all three phases of water (solid, liquid, and gas) coexist in equilibrium. It is used as a reference point in the calibration of thermometers and pressure gauges.
